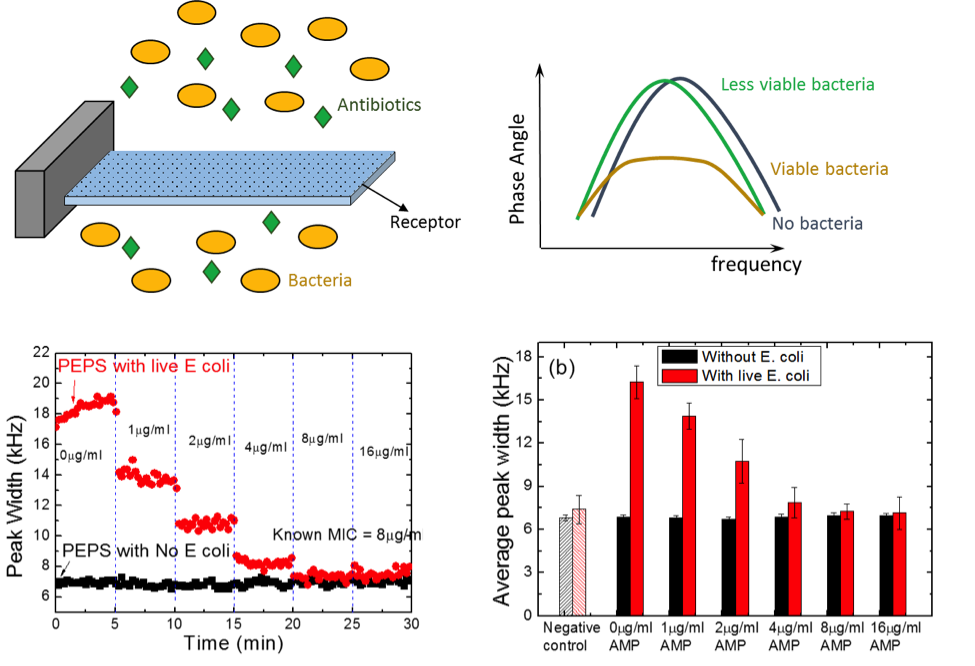
Instant Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test (iAST)
Current antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST) methods all rely on using bacterial growth as a measure to assess how susceptible the bacteria are to the antibiotic drug. As such, they all require incubating the bacteria with the antibiotic drug 10 or more hours in order to assess if the bacteria grow in the presence of the antibiotic drug, prohibiting timely administration of the proper antibiotic at the right dosage, which lengthens the hospital stay and increases the mortality rate. Due to the high sensitivity of PEPS, viable bacteria coated on a PEPS surface impart electrical stresses on the PEPS and flatten the top of its resonance peak. Our lab has successfully used this unique manifestation of PEPS to develop an instant phenotypical AST (iAST) that phenotypically differentiates antibiotic-inhibited bacteria from viable bacteria by coating the bacteria on a PEPS surface and monitoring the change of the width of the top of a resonance peak of the PEPS with an increasing antibiotic drug concentration and determine the minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) of the antibiotic drug.